RF CHALLENGES
Maximize Spectrum Value

The Rise of 5G
40%+
5G subscription
adoption in North America
50%+
of all traffic
now on 5G in the USA
5X
more traffic
expected in the next 5 years
5G Traffic
5G traffic continues to surge, bringing substantial interference challenges
5G Channels
Dense, urban markets will become congested, even on new mid-band TDD spectrum
Uplink Capacity
Growing uplink-heavy app usage heightens the importance of uplink capacity
QoE Expectations
High spectral efficiency is key to meeting subscriber Quality of Experience expectations
Extending LTE
Mobile Trends in Emerging Markets
Focus on ensuring LTE reach for all subscribers
Additional investments needed for site backhaul capacity
High spectral efficiency is essential to meet QoE targets
RF CHALLENGES
RF Interference on a Global Scale
RF interference is a major challenge for mobile operators, leading to reduced network capacity, degraded user quality of experience, and diminished spectral efficiency.
Sources of RF interference include external sources, External and Internal PIM sources, faulty hardware, overlapping coverage, TDD Self Interference due to Tropospheric Ducting, TDD Loss of Synchronization, and cross-border sources.
The intensity and quantity of RF interference exhibit variations based on geographic region, country, market, and RF band.
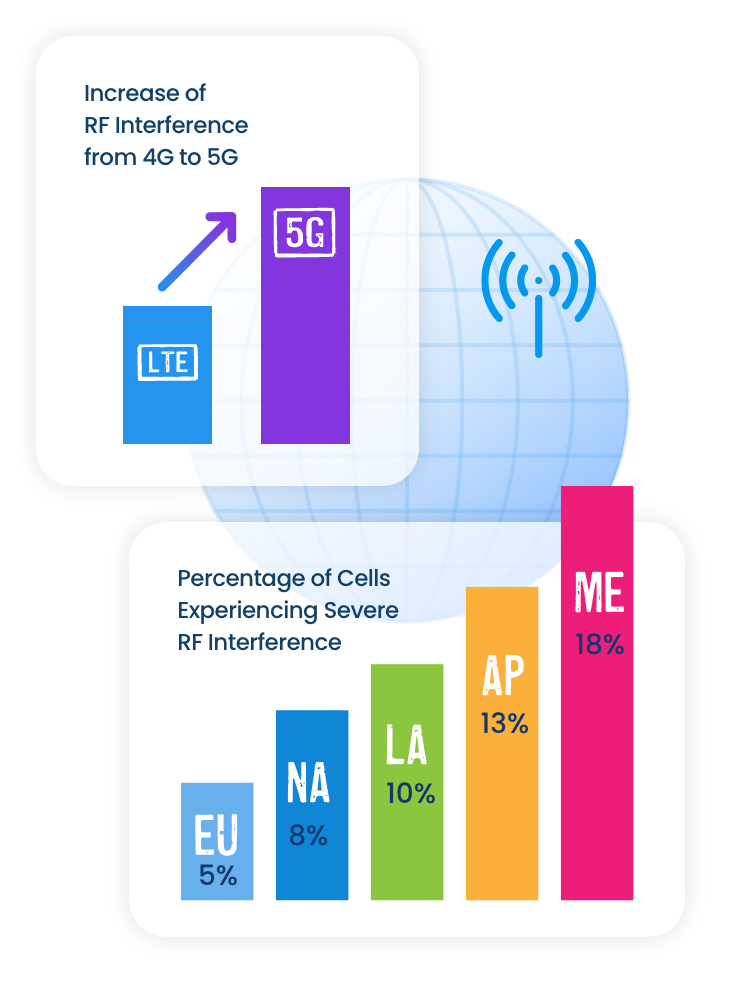
The Cost of RF Interference to Mobile Operators
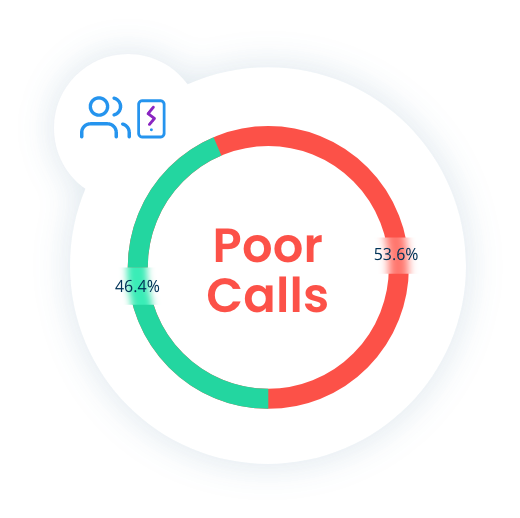
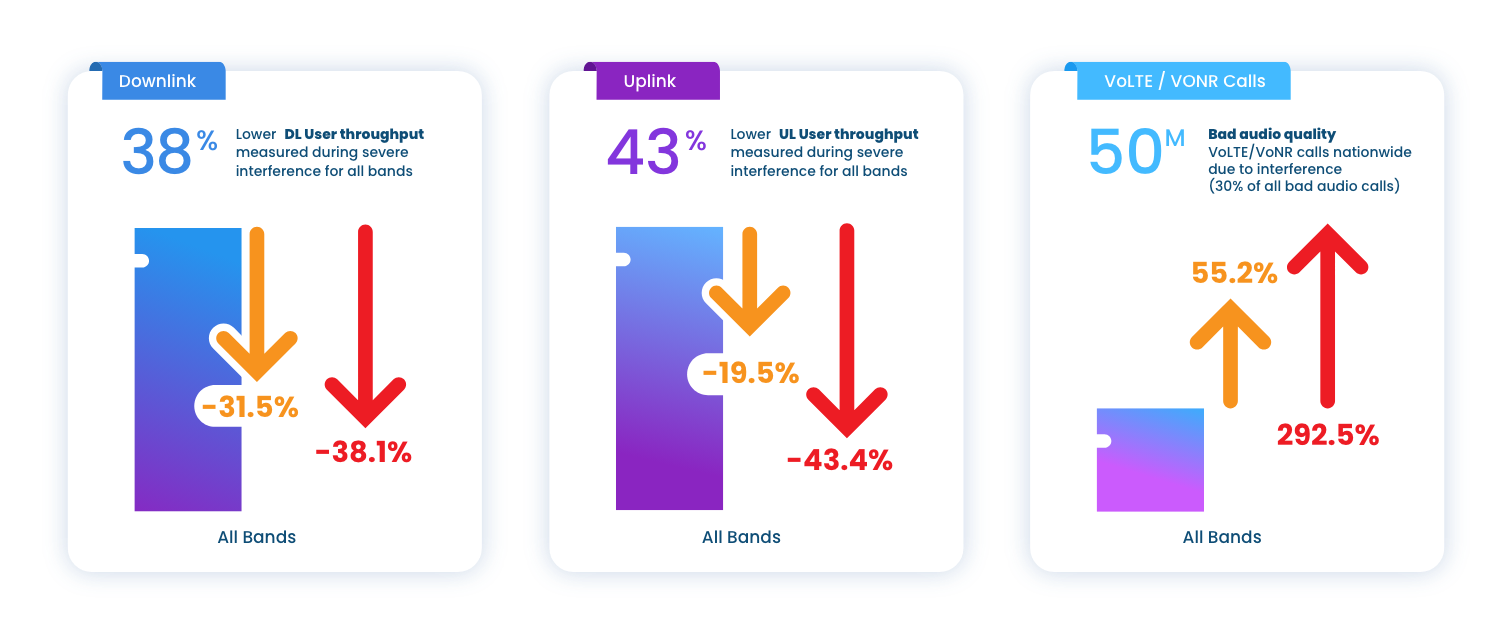
RF interference is the primary contributor to poor user throughput, poor/bad audio quality calls, reduced cell coverage, and poor spectral efficiency in urban areas.
Poor Quality of Experience causes customer dissatisfaction, excessive trouble tickets, and customer churn.
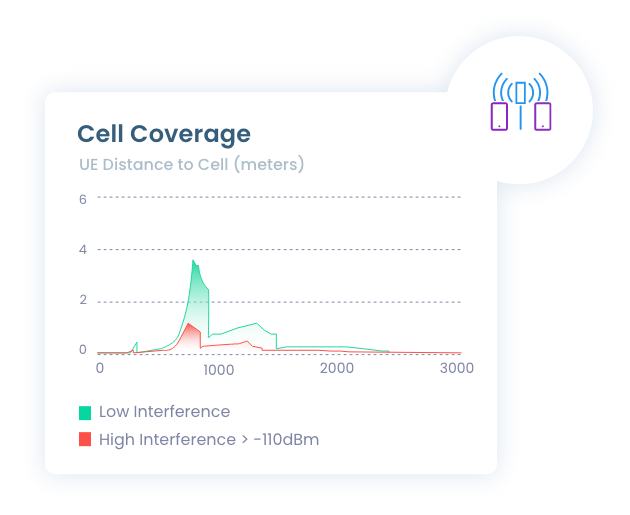
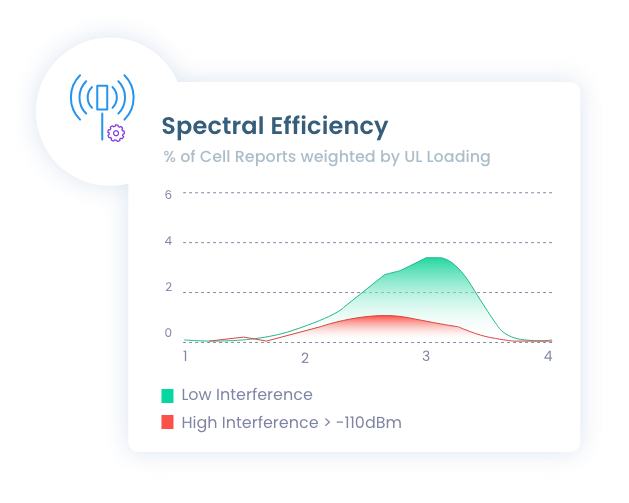
Degraded spectral efficiency diminishes the value of operators’ CAPEX investment in RAN equipment.
Mobile operator legacy processes for addressing interference are cumbersome, manually intensive, inefficient, and ineffective.

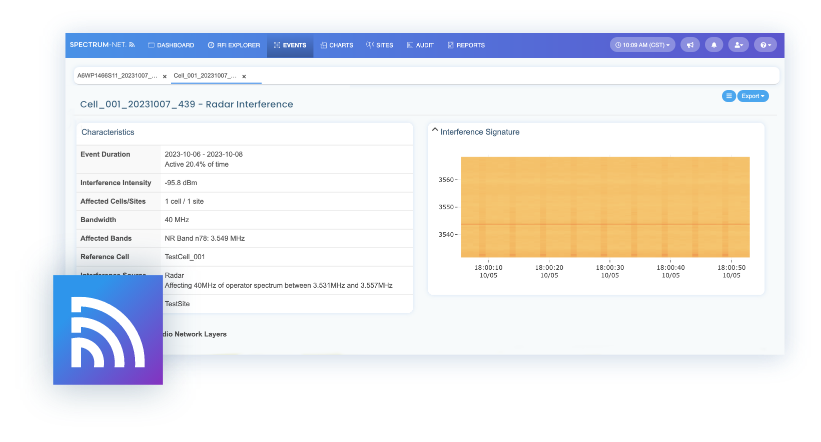
Harness the Power of AI-Driven Interference Mitigation
RF interference costs operators tens of billions of dollars per year globally through inflated OPEX, diminished CAPEX, and heightened subscriber churn. Spectrum-NET empowers operators to auto-mitigate severe interference, instantly improving network KPIs and user quality of experience.
RF CHALLENGES
Addressing the U.S. 5G Mid-Band Spectrum Challenge
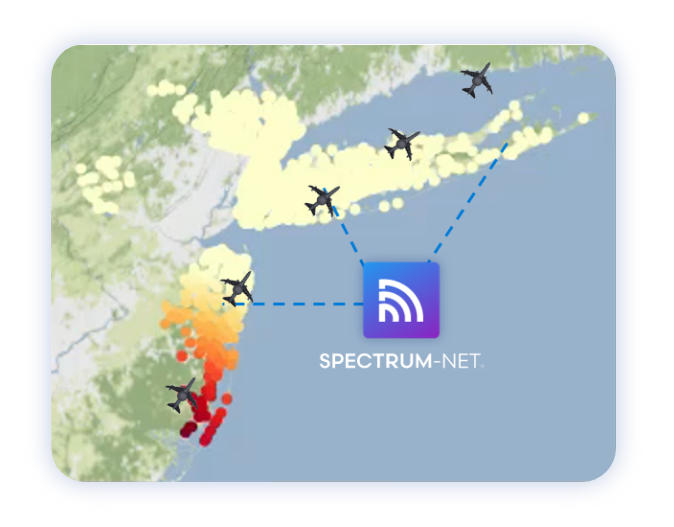
As mobile operators in the USA deploy high-bandwidth 5G channels, utilizing mid-band spectrum such as n41, n77, and n78, challenges are arising due to a deficit in available mid-band spectrum. As highlighted in the recent National Spectrum Strategy Report by the NTIA, the Emerging Mid-Band Radar Spectrum Sharing (EMBRSS) Band, a valuable range of spectrum from 3.1 to 3.45 GHz, is in use by the US Department of Defense while also being vital for 5G expansion.
Recognizing the critical need for mobile operators to access more mid-band spectrum and for the US DoD to preserve its federal mission capabilities and protect incumbent systems, Spectrum Effect is actively researching and developing new Spectrum-NET AI-driven sense-and-maneuver capabilities.

Member of NSC
Ready to see Spectrum-NET in action?
Learn how the world’s leading mobile operators are using Spectrum-NET to drive RF interference mitigation, improve network performance, and maximize spectral efficiency.
Request Network Analysis
